Researchers at the Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences, led by Dr Bhagavatula Prasad and CSIR-National Chemical Laboratory, have developed a method for transforming phenol into 1,4 hydroquinone.
1,4 hydroquinone is used as an intermediate in the manufacturing of food preservatives, pharmaceuticals, dyes, polymers, etc. In addition, oxidation of phenol leads to a huge value addition. India imports phenol worth 23.6 million USD while India spends $56.5M for importing 1,4-hydroquinone. Conventionally, phenol oxidation is carried out by chemical methods using catalysts involving precious metals, metal oxides, and enzymes along with hazardous oxidants. But these methods suffer from many disadvantages, including incomplete conversion of starting material and lack of product selectivity along with environmental hazards.
Dr Prasad has found out that electrolysis is an effective way to carry out the oxidative transformation of phenol to 1,4 hydroquinone.
Electrochemical organic transformations are being looked at with great interest these days because of the economic and environmental advantages they offer over conventional chemical transformation methods. As these transformations are typically carried out in an aqueous medium by just passing electricity through the substrate (in this case phenol), no environmentally hazardous oxidants/reductants are involved in this process. Though electrochemical transformations offer so many advantages, there are several practical issues, especially with respect to phenol oxidation.
For example, the conventional metal-based electrodes could not be used for this transformation as they start losing activity over time due to the adsorption of the oxidized products on their surfaces. Furthermore, many times they lead to over oxidation of phenol resulting in lack of product selectivity and unwanted product formation (tar). Additionally, some of the electrodes also suffer with issues like physical stability and durability of the electrodes with time.
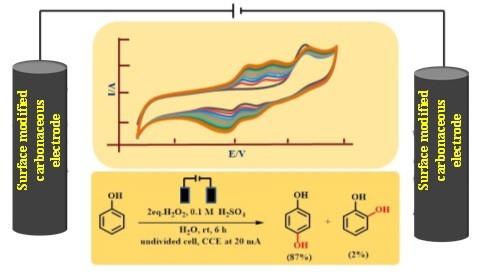
Through detailed cyclic voltametric studies, the NCL and CeNS researchers established all these difficulties could be overcome using electrodes having disordered graphene-like structures with desired number of oxygen-bearing surface functional groups such as hydroxyl (-C-OH), carboxyl (-COOH), and carbonyl (-C=O) groups. The surface modification could be achieved again by electrochemical treatment of the electrode in an acidic environment. Based on systematic studies using techniques like Raman spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, the researchers established optimum conditions for this surface modification. With such appropriately surface-modified carbonaceous electrodes, the conversion of phenol was excellent (99%) with 87% selectivity to 1,4-hydroquinone.
For further details, contact:
Dr. Bhagavatula Prasad pl.bhagavatula@cens.res
Also read:
Technology for making useful products from dried mango leaves
How to make yoga mats from water hyacinth
How to become a hydrogen entrepreneur
Technology to extend shelf-life of sugarcane juice
Seaweed farming — a lucrative business opportunity